LEADING THE INDUSTRY BEYOND INCUMBENT TECHNOLOGIES
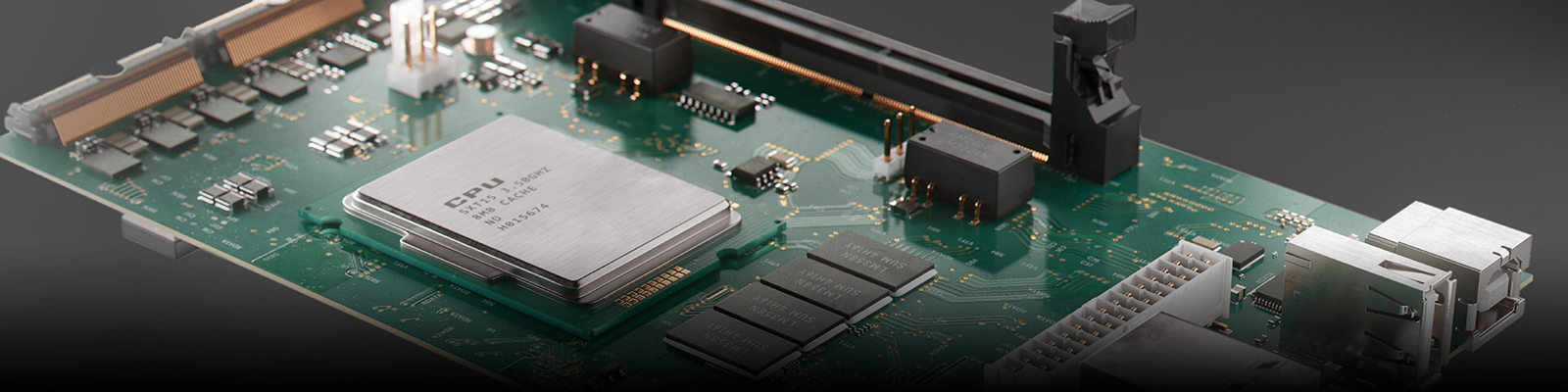
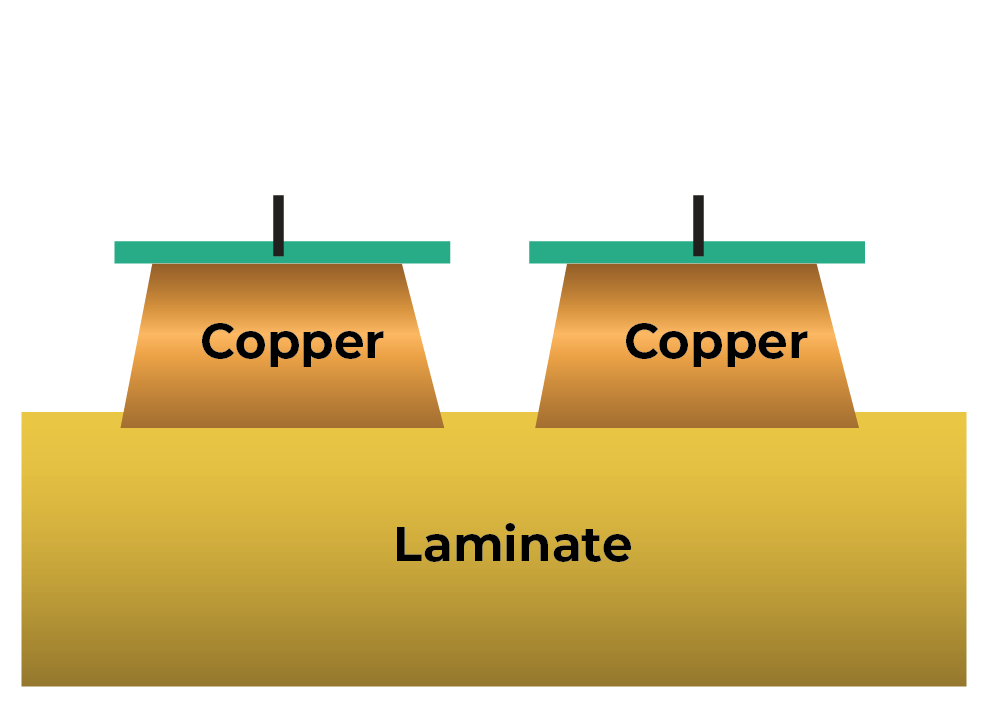
PCT’s Revolutionary Technology is redefining the future of advanced ultra high-density circuit fabrication. By leveraging advanced high-performance materials and innovative additive manufacturing processes, we achieve unparalleled miniaturization of circuit geometry and signal integrity. Moreover, our commitment to environmental sustainability ensures that our advanced fabrication techniques are not only leading the industry but also minimizing environmental impact.